What is RFID technology - a definition and how it works
Radio Frequency Identification, or RFID, is a proven technology that provides numerous solutions for companies: contactless payment, managing physical assets, protecting those assets, and more. Here is a definition of RFID, how it works, its applications and its benefits.
Contents:
- A definition of RFID technology
- How does RFID technology work?
- What are the applications for RFID?
- The benefits of RFID
A definition of RFID technology
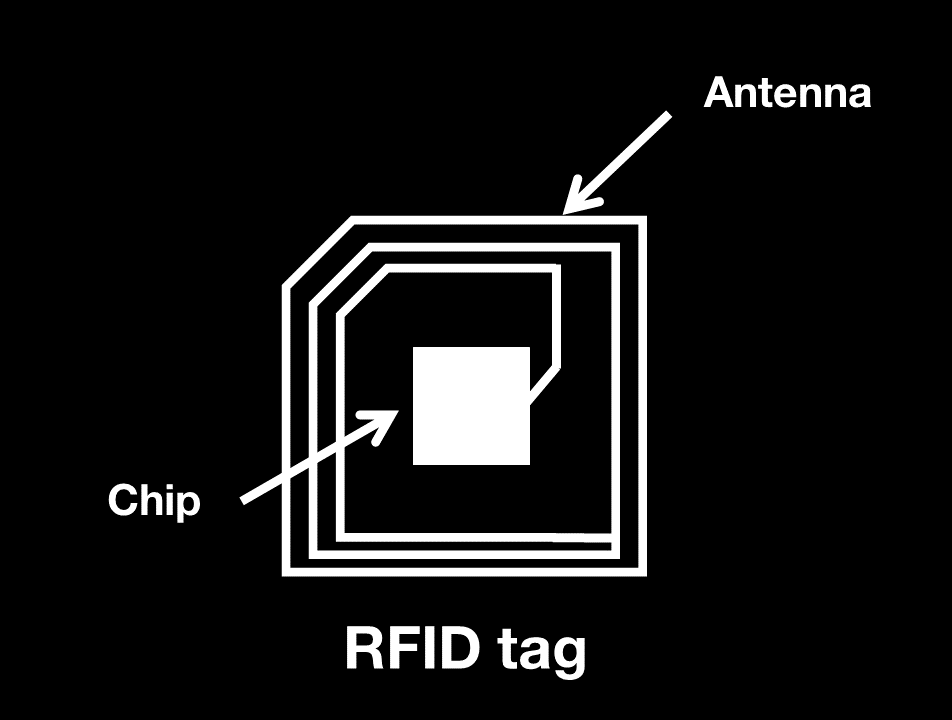 |
RFID is the acronym for Radio Frequency Identification. It is a technology that uses high frequency radio waves to transmit and remember data, with the aim of providing objects, animals, or people with a unique identity. The first applications of RFID go all the way back to the 1930s, when the British wanted to be able to tell the difference between Allied aircraft and the enemy on their radar in real time. The technology then evolved to become the RFID we recognise today. It is used for tracking objects, contactless payments, and more. Radio frequency identification is very useful in numerous applications, particularly the Internet of Things and Big Data. Physically, an RFID tag is most often a flat square (like a patch) with an antenna and an electronic chip on a substrate. |
How does RFID technology work?
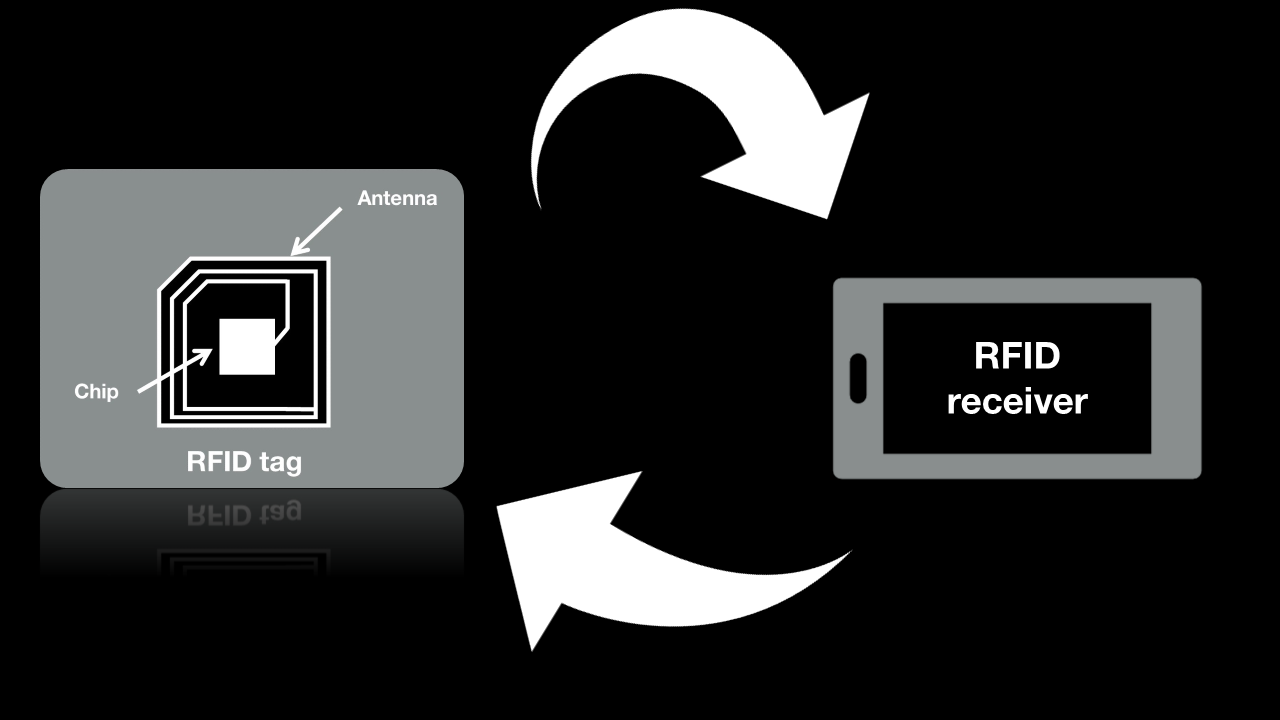 |
Each RFID system is made up of three parts:
The scanning antenna and the emitter-receiver together make up the RFID reader, or RFID interrogator. This can be fixed or mobile and is connected to a communication network. The transponder (label or tag) is an RFID chip that is activated by the energy generated by the radio waves emitted by the reader. The reader interrogates the transponder, which sends back the data requested. |
The tags can be passive, active, or semi-active:
- Passive tags work thanks to energy transferred by electromagnetism, and do not need a battery.
- Active tags include a small battery, to be able to signal over longer distances and record new data.
- Semi-active tags fall in between. Like passive tags, they only send a signal if triggered by an RFID reader. But unlike an active tag, they are not continuously emitting.
Note that several frequency bands can be used and that the highest can be used to increase both the signalling speed and the volume of data.
The signalling distance between RFID readers and tags can vary from a few centimetres to several metres. Some RFID readers and their RFID tags can be used for checks at distances of up to 200 metres. So, the applications can vary enormously.
What are the applications for RFID?
RFID technology was first used by the military. Then, following its development, it was applied in the private sector, especially in industry from the 1980s after the invention of the microprocessor (electronic chip).
RFID applications in everyday life
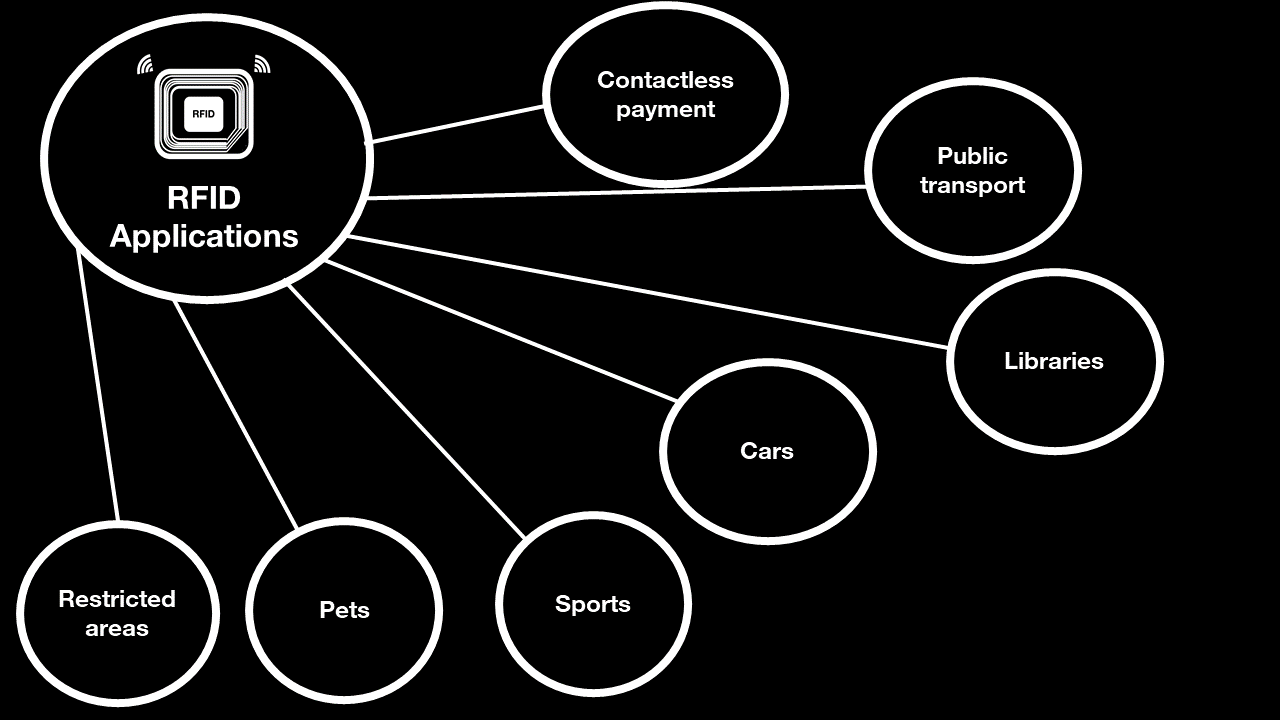 |
RFID systems are a solution that can make everyday life easier:
RFID technology is also being used for the new generation of biometric passports and identity cards. |
RFID applications in trade and industry
The system is also very widely used in industrial and commercial sectors. In commerce there are numerous mechanisms based on RFID that are used for:
- Product inventory with rapid identification
- Simultaneous reading of several items at the till
- Re-stocking alerts for empty shelves, and more.
In the industrial sector there are many benefits:
- monitoring logistics chains
- tracking tools
- traceability of assembly tests
- quickly and easily identifying a production batch, which is especially useful when there is a malfunction and potential health risk
- managing warehouses, etc.
The benefits of RFID
Like all technologies, RFID offers benefits, for instance:
- The need for handling and manoeuvring is reduced: RFID is designed to cut down interaction times (contactless payment, contactless inventories, etc.).
- It simplifies life, with no need to seek out contact points or labels to read, unlike bar codes and QR codes.
- RFID tags can be very small, and so integrated anywhere, even into a thin bank card, into clothing, or under the skin of an animal.
- Connected to the internet with Wi-Fi, RFID technology can be used to transfer data securely over very long distances.
See also: